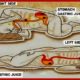
Gullet or esophageal pain, also medically termed as esophagitis refers to the inflammation of the lining of the esophagus.
Gastroesophageal Reflux
According to Nev Dgp, gullet pain is usually caused by the digestive juices in the stomach, which repeatedly go up to the lower part of the esophagus. Medically, it is called esophageal acid reflux. As per the publication, the contractions of the muscles usually keep the lower end of the esophagus closed; however, weak esophageal muscles can lead to acid reflux. According to Medicine Net, the condition may cause irritation of the esophagus inner linings, hence it is called gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD. As per the publication, it may escalate to erosive esophagitis in severe cases.
In line with acid reflux, vomiting can also lead to gullet pain. Vomitus contain gastric content from the stomach; thus, frequent or chronic vomiting episodes may result to acid damage to the esophagus. Also, excessive or forceful vomiting may also causes minute tears in the esophagus’ inner lining, which results to further damage.
Neuromuscular Disorder
Impaired neuromuscular function can also cause gullet pain. According to Web MD, the cause of esophageal spasm remains unknown, but several doctors agree that is it caused by an interruption of the nerve activity that innervates the esophagus’ swallowing action. Along with impulse issues, the temperature of that food a person eats may lead to the spasm. As per the publication, very hot or very cold foods may lead to the spasmodic episode.
Hiatal Hernia
Gullet pain may also be due the reflux secondary to the presence of hiatus hernia, which is the protrusion of a small part of the stomach above the diaphragm into the chest. As per Nev Dgp, this prevents the muscle at the bottom part of the esophagus from performing its functions. According to Medicine Net, such structural abnormality may result to too much acid refluxing into the esophagus.
Surgery and Medications
Another potential cause of gullet pain is surgery. According to Medicine Net, some types of weight loss or bariatric surgery can result to a higher risk of esophagitis. This may be related to the surgical procedure, as well as the anesthetic agent used to relax the muscles of the body, which includes the esophageal muscles.
Along with surgery, medications may also contribute to esophageal pain. As per the publication, medications like aspirin and some anti-inflammatory agents may result to esophageal lining irritation and increased acid production in the stomach. As a further effect, it can lead to acid reflux. In addition, medications in oral pill forms, when taken with only small amount of water or prior to going to bed can dissolve and get stuck in the esophagus and this leads to irritation.
Infection
Infection is another potential cause of gullet pain, as per Medicine Net. According to he publication, bacteria, fungi, and viruses may irritate the esophagus, which leads to the pain sensation. As per the publication, one cause is the yeas infection Candida, which is more common in patients with diabetes, weak immune system, HIV or AIDs, and cancer. People who are undergoing chemotherapy and those who are taking antibiotics or steroids may also experience gullet pain. Another infection is herpes, which is a viral infection, unlike the fungal Candidiasis. This infection also develops in the person’s esophagus due to a weak immune system.
Food and Lifestyle
While the major cause of esophageal muscle weakness, it is viewed that factors, such as excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, lead to gullet pain. Food also contributes to gullet pain. As per the Nev Dgp, certain food choices, such as acidic, spicy, and fatty foods are the culprit. In addition, wearing tight clothing and being overweight also elevates the pressure on the junction between the esophagus and the stomach, thus, resulting to the reflux.
Overall, gullet pain has several contributing factors, though researchers have not found the exact cause of the condition. Hence, it is best to consult a health professional, if concerns related to the aforementioned factors arise.