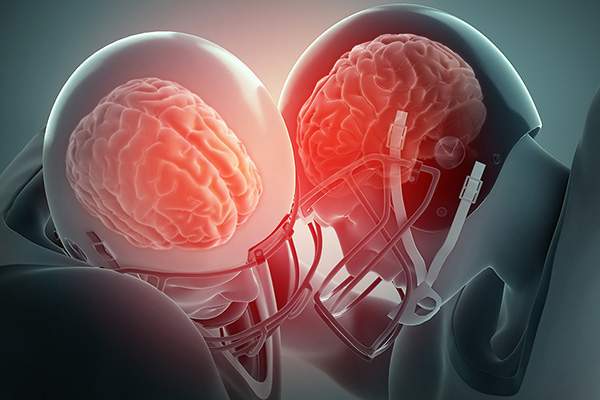
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy or CTE refers to a condition of the brain stemming from repeated blows to the head. While it’s true that it is something that is highly associated with football players, many other types of athletes are at risk of having it, too, such as those who are involved in football, ice hockey, wrestling and boxing.
Speaking of boxing, in the past CTE was closely related to the so-called “punch-drunk syndrome”. Experts found out that repeated blows to a boxer’s head was more significant in the development of the said syndrome rather than the number of times ending up knocked out in a boxing ring.
To date, there is no known formal way to have CTE diagnosed since it is regarded as relatively new. The only way to reveal if CTE is the cause of the death of someone who is suspected to have it is by means of an autopsy. Similarly, there is no treatment available for this brain condition affecting so many individuals who engage in contact sports.
Causes
According to experts, CTE is caused by repeated blows to the heads or concussions. They add that even the kind of direct trauma to the head that does not lead to unconsciousness may also cause CTE to transpire.
Unfortunately, the use of harder and safer helmets cannot prevent CTE from striking, experts say. That’s because the use of such headgear won’t really prevent the brain from moving back and forth inside an athlete’s brain, thus resulting in sub-concussive hits, which are known to be as risk factors for CTE.
The said sub-concussive hits can result in the abnormal buildup of tau, which is a type of protein, in the brain. Eventually, the said accumulation of tau can take over certain parts of an athlete’s brain.
So what’s the problem with such buildup? Well, it’s something that can lead to the death of brain cells. Basically, it is the same thing that happens to a person who has Alzheimer’s disease, which is characterized by the collection of certain types of protein in the brain, such as tau and beta-amyloid.
However, experts say that this does not mean that all individuals who partake in contact sports will end up having CTE. They suspect that factors such as the genes and environment are role players, too, in CTE development.
Signs and Symptoms
Just like what’s mentioned earlier, CTE is a relative newcomer in the world of medicine, and that is why experts do not really understand all of the aspects of CTE — more research is necessitated, they say.
However, they do know that CTE tends to produce signs and symptoms that are similar to conditions characterized by a significant loss in the number of brain cells, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. It’s for this reason why someone with CTE may exhibit:
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Personality changes
- Unpredictable behavior
- Confusion
- Loss of memory
- Problems organizing thought
- Vision problems
- Speech trouble
- Difficulty in paying attention
- Tremors
Experts do not really know the complete signs and symptoms associated with CTE. It’s for the fact that the brain condition is still currently being researched intensively.
Treatment
Again, there is no available treatment for CTE yet. Experts, as of now, suggest that keeping trauma to the head, especially the repeated kind, to a minimum can help lower a person’s risk of having CTE in the future.
By the way, there is no way to diagnose CTE in people who are suspected to have it and are still living. The only means of confirming whether or not CTE is present is by taking a look at the brain during autopsy. In other words, it is only when the individual is already dead that the presence of CTE can be confirmed.